Uploading files¶
You can head to the Files tab to manage your files. From there, you will be able to upload new files (from your local computer, or a remote endpoint), and delete them.
Warning
Deleting files does not delete related datasets.
Data visibility¶
By default, all your uploaded files and datasets are private.
If you have administrator privileges, you can select the
Info
Public datasets will be queriable by any user, including non-logged users. They will not be able to directly access the file, but generated entities will appear on the query graph (and on the starting screen for starting entities).
Warning
Make sure your public datasets do not contain sensitive information.
CSV/TSV files¶
AskOmics will integrate a CSV/TSV file using its header. The type of each column will be predicted, but you will be able to modify it before integration.
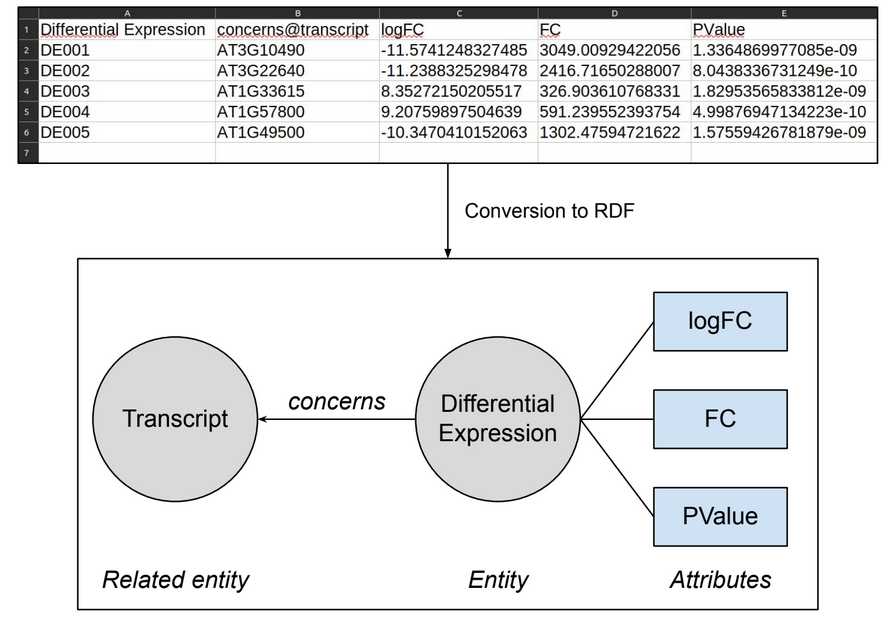
Entity (first column)¶
Entity URI¶
The first column of the file will manage the entity itself : the column name will become the entity name, and the values will become the entity's instances URIs.
URIs will be created as follows :
- If the value is an URL, it will be integrated as it is.
- If the value is a CURIE, it will be transformed into an URL before integration. The list of managed CURIE formats is available here.
- Else, the value will be added to either AskOmics namespace_data value, or a custom base URI if specified in the integration form.
Warning
Unless you are trying to merge entities, make sure your URIs are unique across both your personal and public datasets.
Entity type¶
The entity type can either be "starting entity", or "entity". If "starting entity", it may be used to start a query on the AskOmics homepage. Both types will appear as a node in the AskOmics interface.
Inheritance¶
The entity can inherit the attributes and relations of a 'mother' entity. Meaning, you will be able to query the sub-entity on both its own, and its 'mother' attributes and relations. The 'mother' entity however will not have access to any 'daughter' attributes or relations.
To setup inheritance, the column name needs to be formated as follows:
- daughter_entity_name < mother_entity_name (with the < symbol)
ie: Custom_population < General population
Warning
The values of this column must be an URI of the mother entity
Entity label (first and second column)¶
To manually set an entity label, you can set the second column as a Label column.
The values of this column will be used as labels for the generated entities.
Warning
If a value is missing in the column, the label will be created based on the entity URI. (See below)
If there is no Label column, the labels will be generated based on the URIs (The first column).
- If the value is an URL, the last non-empty value after a "/" or "#" will be the label.
- If the value is a CURIE, the value after ":" will be the label
- Else, the raw value is the label
Info
For example, a one-column CSV file with the column name "Gene", and the values "gene1", "rdfs:gene2" and "http://myurl/gene3/" will create the entity Gene, with two instances labelled gene1, gene2 and gene3.
Attributes¶
Each column after the first one will be integrated as an attribute of the entity. The column name will be set as the name of the attribute.
Several attribute types are available. The type of an attribute will dictate the way it will be managed in the query form (eg: text field, value selector...)
!!! note 'Info' AskOmics will try to guess the type of a column based on its name and its values. You will be able to set it manually if the auto-detected type doesn't fit.
Attributes can be of the following types :
Base types¶
- Numeric: if the values are numeric
- Text: if all values are strings
- Date: if all values are dates (using dateutil.parser)
- Auto-detected terms are 'date', 'time', 'birthday', 'day'
- Category: if there is a limited number of repeated values
- Boolean: if the values are binary ("True" and "False", or "0" and "1")
Warning
If the date format is ambiguous (eg: 01/01/2020), AskOmics will interpret it as day/month/year
FALDO types¶
If the entity describe a locatable element on a genome (based on the FALDO ontology):
- Reference: chromosome (Auto-detected terms : 'chr', 'ref', 'scaff')
- Strand: strand (Auto-detected terms : 'strand')
- Start: start position (Auto-detected term : 'start', 'begin')
- End: end position (Auto-detected terms : 'end', 'stop')
Warning
To mark an entity as a FALDO entity, you need to provide at least a Start and End columns.
Reference and/or Strand are optional, but will enable more specific queries (eg: Same reference or Same strand)
Relations¶
A column can also symbolize a relation to another entity. In this case, the column name must be of the form :
- relationName@RelatedEntityName (with the @ symbol)
- ie: Derives_from@Gene
Two types are available :
- Directed: Relation from this entity to the targeted one (e.g. A is B’s father, but B is not A’s father)
- Symetric: Relation that works in both directions (e.g. A loves B, and B loves A)
Warning
The content of the column must be URIs of the related entity.
(The related entity and its URIs may be created afterwards)
Linked URIs must match one of these three formats :
- Full URI
- CURIE
- Simple value (the value will transformed into an URI with AskOmics namespace_data value)
This link between entities will show up in the query screen, allowing users to query related entities.
Info
All FALDO entities will be automatically linked with the included_in relation, without needing an explicit link. You can still specify your own relations.
Warning
For federated queries, the syntax is slightly different. Please refer to this page for more information.
GFF files¶
Warning
Only the GFF3 format is managed by AskOmics.
Each GFF file can be integrated into several entities. You will be able to select the entities you wish to integrate beforehand. Available entities are the values of the 'type' column of the GFF file. The relations between entities (eg: Parents or Derives_from) will also be integrated.

Extracted attributes are the following :
- Reference
- Strand
- Start
- End
- Any attribute in the attributes column
- Parents and Derives_from will be converted in relations
Info
All entities extracted from GFF files are FALDO entities, and will be linked implicitly with the included_in relation.
BED files¶
Each BED file will be integrated into one entity (the default entity name will be the file name, but it can be customized).
Extracted attributes are the following :
- Reference
- Strand
- Start
- End
- Score
Info
All entities extracted from BED files are FALDO entities, and will be linked implicitly with the included_in relation.
TTL Files¶
You can integrate TTL files in AskOmics, either to integrate your own data, or to enable federated queries to remote endpoints.
In both case, you will need to generate or convert your data in AskOmics's format.
This can be done either manually or automatically